32. Cannula (Cánula): is a tube which can be inserted into the body, often for the delivery or removal of fluid.

33. Capillary (Capilar): is the smallest of a body's blood vessels, measuring 5-10 μm in diameter, which connect arterioles and venules, and enable the interchange of water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, and many other nutrient and waste chemical substances between blood and surrounding tissues.

34. Capsid (Cápside): is the protein shell of a virus. It consists of several oligomeric structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The 3-dimensional morphological subunits that can be observed, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The capsid encloses the genetic material of the virus.

35. Capsule (Cápsula): is a very large organelle of some prokaryotic cells, such as bacterial cells. It is a layer that lies outside the cell wall of bacteria. It is a well organized layer, not easily washed off, and it can be the cause of various diseases.
36. Cardiac Massage (Masaje cardiaco): technique of cardiac resuscitation.

37. Carcinogen (Carcinógeno): refers to any substance, radionuclide or radiation that is an agent directly involved in the promotion of cancer or in the increase of its propagation. This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke.

38. Chromatin (Cromatina): is the complex combination of DNA, RNA, and protein that makes up chromosomes. It is found inside the nuclei of eukaryotic cells, and within the nucleoid in prokaryotic cells. It is divided between heterochromatin (condensed) and euchromatin (extended) forms. Chromatin contains genetic material-instructions to direct cell functions.

39. Clamp (Pinza): is an instrument used mainly in surgery

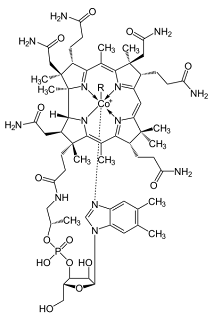
40. Cobalamin (Cobalamina): A complex compound, containing cobalt (a member of the vitamin B complex), found in liver; it is used to treat pernicious anemia.


No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario